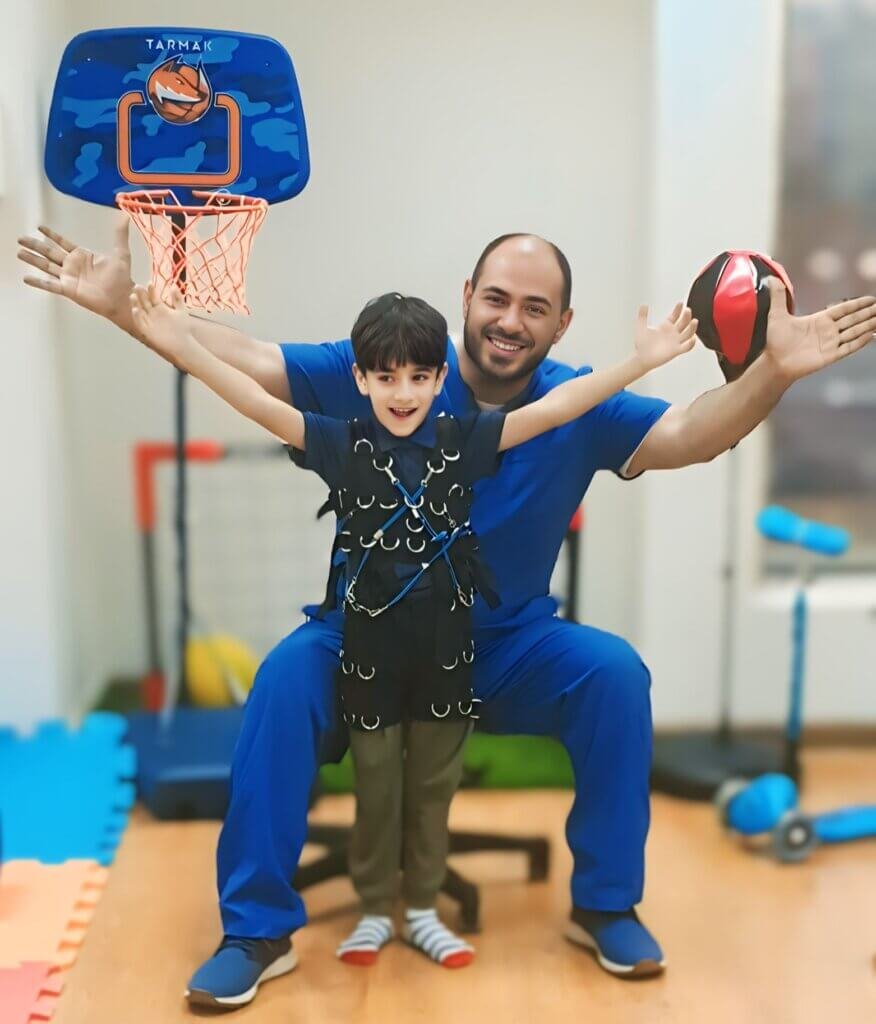
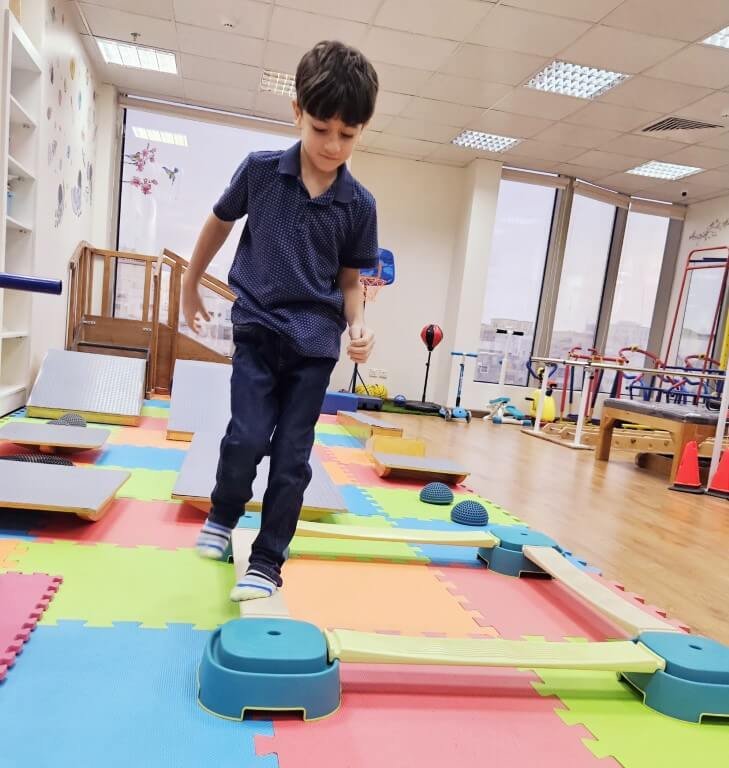
The suspension gym system is a valuable tool in the physical therapist's arsenal, and is frequently used to treat a variety of pediatric conditions such as:
-
- Neuromotor development disorders.
- Motor Developmental Delay: The suspension gym system helps strengthen weak muscles and improve range of motion. It helps children with motor developmental delays develop basic motor skills such as crawling, sitting, standing and walking.
- Cerebral Palsy: Helps improve balance and coordination, improve motor functions, and reduce muscle tension and stress.
- Down Syndrome: Helps strengthen muscles, facilitate movement and develop basic motor skills.
This suspension system is an effective tool for measuring the improvement in the strength and range of motion of a weak or spastic muscle. Using this suspension system of pulleys and weights, even a child who has just been able to move the muscle or limb he wants to move can now develop muscle strength, flexibility and endurance through a series of consecutive sessions provided by our experienced specialists.